When you buy or DIY your own lithium solar battery pack, the most common terms you come across are series and parallel, and of course, this is one of the most asked questions from the FlyKol team. If you have ever worked with batteries you have probably come across the terms,Series, Series-Parallel, and Parallel is the act of connecting two batteries together, but why would you want to connect two or more batteries together in the first place?By connecting two or more batteries in either series, series-parallel, or parallel, you can increase the voltage or amp-hour capacity, or even both; allowing for higher voltage applications or power hungry applications.
For those of you who are new to Lithium solar batteries, this can be very confusing, and with this article, FlyKol, as a professional lithium battery manufacturer, we hope to help simplify this question for you!
Basics
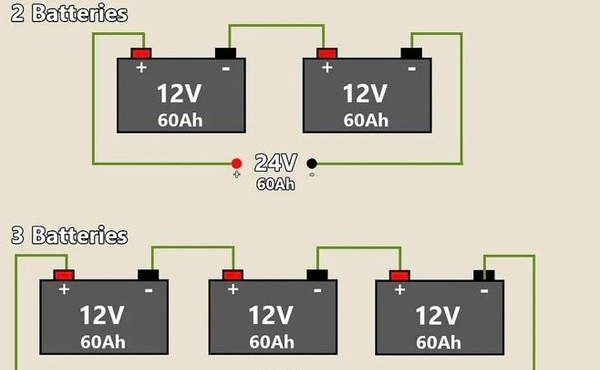
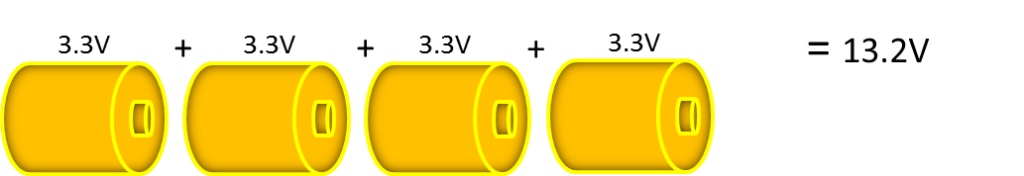
Battery packs are designed by connecting multiple cells in series; each cell adds its voltage to the battery’s terminal voltage. Figure 1 below shows a typical 13.2V LiFePO4 starter battery cell configuration.
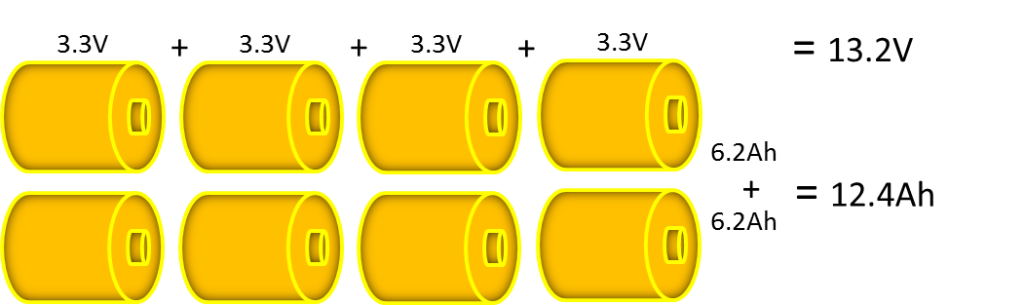
Batteries may consist of a combination of series and parallel connections. Cells in parallel increased current handling; each cell adds to the ampere-hour (Ah) total of the battery The is an example of a series and parallel configuration. The configuration, 13.2V / 12.4Ah, is shown in Figure 2.
A weaker cell in series connected cells would cause an imbalance. This is especially critical in a series configuration because a battery is only as strong as the weakest cell (analogous to the weak link in the chain). A weak cell may not fail immediately but may be drained (voltage dropping below a safe level, 2.8V per cell) more quickly than the strong ones when discharging. On charge, the weak cell may fill up before the healthy ones and be over-charged (voltage exceeding 3.9V per cell). Unlike the weak link in a chain analogy, a weak cell causes stress on the other healthy cells in a battery. Cells in multi-packs must be matched, especially when exposed to high charge and discharge currents. Figure 3 below shows an example of a battery with a weak cell.
How to Connect Lithium Ion Batteries in Parallel
What is Series and Parallel Connection?
Actually, in simple terms, connecting two (or more) batteries in series or parallel is the act of connecting two (or more) batteries together, but the harness connection operations performed to achieve these two results are different. For example, if you want to connect two (or more) LiPo batteries in series, connect the positive terminal (+) of each battery to the negative terminal (-) of the next battery, and so on, until all LiPo batteries are connected. If you want to connect two (or more) lithium batteries in parallel, connect all positive terminals (+) together and connect all negative terminals (-) together, and so on, until all lithium batteries are connected.
Why do You Need to Connect the Batteries in Series or Parallel?
For different lithium solar battery applications, we need to achieve the most perfect effect through these two connection methods, so that our solar lithium battery can be maximized, so what kind of effect do parallel and series connections bring to us? The main difference between the series and parallel connection of lithium solar batteries is the impact on the output voltage and battery system capacity.
Lithium solar batteries connected in series will add their voltages together in order to run machines that require higher voltage amounts. For example, if you connect two 24V 100Ah batteries in series, you will get the combined voltage of a 48V lithium battery. The capacity of 100 amp hours (Ah) remains the same. However, it is important to note that you must keep the voltage and capacity of the two batteries the same when connecting them in series, for example, you cannot connect a 12V 100Ah and 24V 200Ah in series!
What are the benefits of connecting solar lithium batteries in series?
Firstly, series circuits are easy to understand and build. The basic properties of series circuits are simple, making them easy to maintain and repair. This simplicity also means that it is easy to predict the behavior of the circuit and calculate the expected voltage and current.
Secondly, for applications that require high voltages, such as a home three-phase solar system or industrial and commercial energy storage, series-connected batteries are often the better choice. By connecting multiple batteries in series, the overall voltage of the battery pack increases, providing the required voltage for the application. This can reduce the number of batteries needed and simplify the design of the system.
Thirdly, series-connected lithium solar batteries provide higher system voltages, which result in lower system currents. This is because the voltage is distributed across the batteries in the series circuit, which reduces the current flowing through each battery. Lower system currents mean less power loss due to resistance, which results in a more efficient system.
Fourthly, circuits in series do not overheat as quickly, making them useful near potentially flammable sources. Since the voltage is distributed across the batteries in the series circuit, each battery is subjected to a lower current than if the same voltage were applied across a single battery. This reduces the amount of heat generated and lowers the risk of overheating.
Fifthly, higher voltage means lower system current, so thinner wiring can be used. The voltage drop will also be smaller, which means that the voltage at the load will be closer to the nominal voltage of the battery. This can improve the efficiency of the system and reduce the need for expensive wiring.
Finally, in a series circuit, current must flow through all components of the circuit. This results in all components carrying the same amount of current. This ensures that each battery in the series circuit is subjected to the same current, which helps to balance the charge across the batteries and improve the overall performance of the battery pack.
What are the Disadvantages of Connecting Batteries in Series?
Firstly, when one point in a series circuit fails, the entire circuit fails. This is because a series circuit has only one path for current flow, and if there is a break in that path, the current cannot flow through the circuit. In the case of compact solar power storage systems, if one lithium solar battery fails, the entire pack may become unusable. This can be mitigated by using a battery management system (BMS) to monitor the batteries and isolate a failed battery before it affects the rest of the pack.
Secondly, when the number of components in a circuit increases, the resistance of the circuit increases. In a series circuit, the total resistance of the circuit is the sum of the resistances of all the components in the circuit. As more components are added to the circuit, the total resistance increases, which can reduce the efficiency of the circuit and increase the power loss due to resistance. This can be mitigated by using components with lower resistance, or by using a parallel circuit to reduce the overall resistance of the circuit.
Thirdly, series connection increases the voltage of the battery, and without a converter, it may not be possible to get a lower voltage from the battery pack. For example, if a battery pack with a voltage of 24V is connected in series with another battery pack with a voltage of 24V, the resulting voltage will be 48V. If a 24V device is connected to the battery pack without a converter, the voltage will be too high, which can damage the device. To avoid this, a converter or voltage regulator can be used to reduce the voltage to the required level.
What are the Benefits of Connecting Batteries in Parallel?
One of the main advantages of connecting lithium solar battery banks in parallel is that the capacity of the battery bank increases while the voltage remains the same. This means that the run time of the battery pack is extended, and the more batteries that are connected in parallel, the longer the battery pack can be used. For example, if two batteries with a capacity of 100Ah lithium batteries are connected in parallel, the resulting capacity will be 200Ah, which doubles the run time of the battery pack. This is especially useful for applications that require a longer run time.
Another advantage of a parallel connection is that if one of the lithium solar batteries fails, the other batteries can still maintain power. In a parallel circuit, each battery has its own path for current flow, so if one battery fails, the other batteries can still provide power to the circuit. This is because the other batteries are not affected by the failed battery and can still maintain the same voltage and capacity. This is particularly important for applications that require a high level of reliability.
What are the Disadvantages of Connecting Lithium Solar Batteries in Parallel?
Connecting batteries in parallel increases the total capacity of the lithium solar battery bank, which also increases the charging time. The charging time may become longer and more difficult to manage, especially if multiple batteries are connected in parallel.
When solar lithium batteries are connected in parallel, the current is divided among them, which can lead to higher current consumption and higher voltage drop. This can cause problems, such as reduced efficiency and even overheating of the batteries.
Parallel connection of solar lithium batteries can be a challenge when powering larger power programs or when using generators, as they may not be able to handle the high currents produced by the parallel batteries.When lithium solar batteries are connected in parallel, it can be more difficult to detect defects in the wiring or the individual batteries. This can make it harder to identify and fix problems, which can result in reduced performance or even safety hazards.
Battery Management System (BMS) Cell Protection
A BMS continuously monitors each cell’s voltage. If the voltage of a cell exceeds the others, the BMS circuits will work to reduce that cell’s charge level. This ensures that the charge level of all the cells remains equal, even with the high discharge (> 100Amps) and charge current (>10Amps).
A cell can be permanently damaged if over-charged (over-voltage) or over-discharged (drained) just one time. The BMS has circuitry to block charging if the voltage exceeds 15.5 volts (or if any cell’s voltage exceeds 3.9V). The BMS also disconnects the battery from the load if it is drained to less than 5% remaining charge (an over-discharge condition). An over-discharged battery typically has a voltage less than 11.5V (< 2.8V per cell).
Multiple Batteries In Series And Or Parallel (Each Battery With Its Own BMS)
EarthX batteries are approved for use in applications with up to two batteries in parallel, with no additional external electronics. The restriction to two batteries allows for normal variations in one battery without adversely affecting the other battery. For applications with more than two batteries in parallel, please contact EarthX tech support.
EarthX batteries are NOT approved for series operation without engineering design and approval. This restriction is due to the fact that impedance, capacity, or self-discharge rates vary between cells and between batteries. EarthX offers many 26.4 volt batteries. It is always preferred to use a single 26.4 volt battery versus two 13.2 volt batteries in series, for the single battery can internally monitor each of the 8 cells in series and ensure the charge level of all cells are balanced.
Parallel Operation
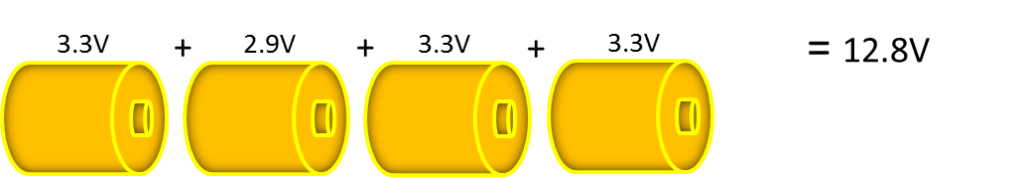
Like individual cells, you can combine batteries together in parallel to achieve higher energy/power (amp-hours, amps). Up to two batteries can be put in parallel. To combine batteries in parallel, connect positive to positive and negative to negative as shown in Figure 4 right.
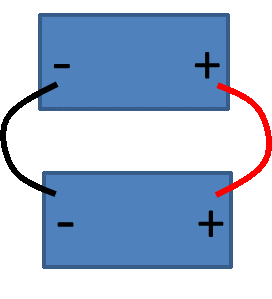
It is important to use the same battery model with equal voltage and never to mix batteries of a different age.
When connecting two batteries, it is important to make sure the charge levels are similar (voltages are within 0.3 volt) before connection. If there is a large difference in charge level, high current can flow between the batteries.
In situations where the batteries are automatically connected/disconnected there must be external equipment to limit the current to less than the batteries maximum charge current specification and/or interconnecting wire ampacity specification.
Series Operation
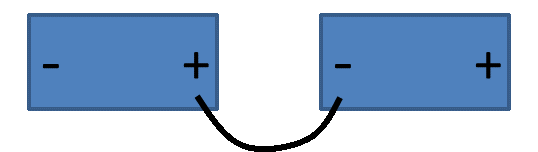
Unlike parallel operation, series operation or series/parallel operation requires thoughtful engineering and maintenance to make the system function properly. Contact engineering for design approval. It is important to use the same battery model with equal voltage and capacity (Ah) and never to mix batteries of a different age. Both batteries in a series configuration must have the EXACT same load, meaning you cannot connect a load to just one battery in the series. If you charge one battery you must charge the other to an equal charge level. If you replace one battery, you must replace the other battery. See the example below for series wiring (Figure 5).
SERIES / PARALLEL OPERATION
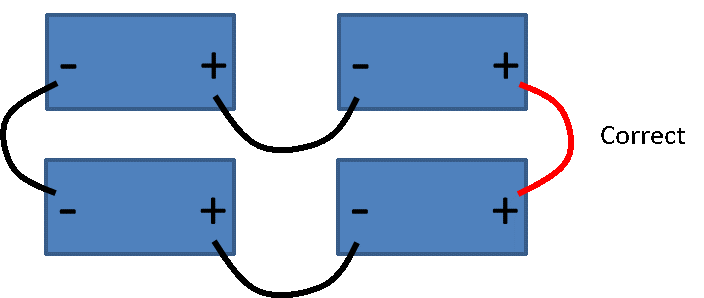
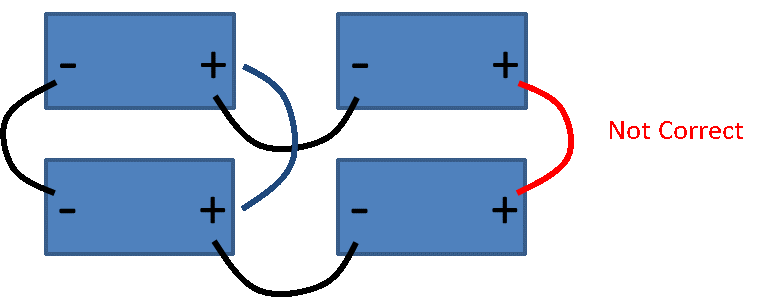
Below is the approved series and parallel configuration (Figure 6). The batteries are wired as two separate series battery paths, meaning there is no cross ties between the centers of the two separate paths. Figure 7 shows an incorrect connection with a cross tie between the centers of the two separate series paths.
Is it Possible to Connect Lithium Solar Batteries both in Series and in Parallel?
Yes, it is possible to connect lithium batteries in both series and parallel, and this is called a series-parallel connection. This type of connection allows you to combine the benefits of both series and parallel connections.
In a series-parallel connection, you would group two or more batteries in parallel, and then connect multiple groups in series. This allows you to increase the capacity and voltage of your battery pack, while still maintaining a safe and reliable system.
For example, if you have four lithium batteries with a capacity of 50Ah and a nominal voltage of 24V, you could group two batteries in parallel to create a 100Ah, 24V battery pack. Then, you could create a second 100Ah, 24V battery pack with the other two batteries, and connect the two packs in series to create a 100Ah, 48V battery pack.
Series and Parallel Connection of Lithium Solar Battery
A combination of a series and a parallel connection allows greater flexibility to achieve a certain voltage and power with standard batteries. The parallel connection gives the required total capacity and the series connection gives the desired higher operating voltage of the battery storage system.
Example: 4 batteries with 24 volts and 50 Ah each result in 48 volts and 100 Ah in a series-parallel connection.
Series / Parallel Operation And Fault Indication
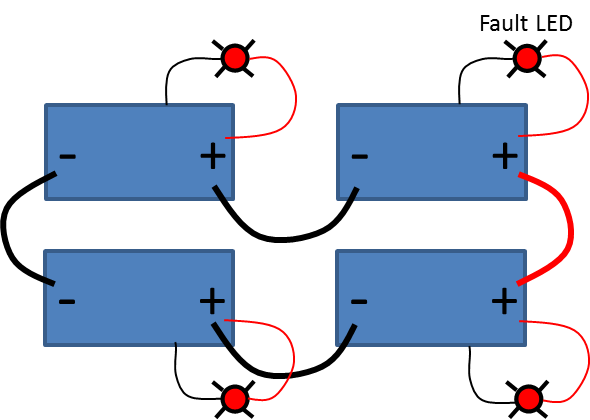
Each EarthX battery requires its own remote fault indication LED. The 12V LED is connected across the battery’s positive terminal and the remote fault indicator wire (pigtail wire out the side of the battery), see Figure 8 below. Connecting the remote fault indicator to an EFIS is not an option in any series configuration (12V LED light is the only option).
Series / Parallel Operation Charging (Maintenance)
With an approved engineering design, when using two 13.2 volt batteries in series, it is most important to keep the two batteries matched. If charging is needed, both batteries must be charged to an equal level. If a battery needs to be replaced, both batteries must be replaced. Both batteries must have matching capacity, and charge level always.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does connecting batteries in parallel increase amp hours?
Yes. When you connect your batteries in parallel, you increase the amp-hour capacity of your batteries. The voltage stays the same.
For example, let’s say you connect two 12v 100ah batteries in parallel. It’ll stay a 12 volt system, but the amps will double to 200ah. And of course, the batteries will last a lot longer.
What happens when you put two 12 volt batteries in series?
When you have two or more 12 volt batteries hooked up in series, you develop 24 volts, but your amps don’t change. On the other hand, if you have those 12 volt batteries wired in parallel, it’s still a 12 volt system, but the amps will increase. (See example in the section below.)
Do batteries last longer in series or parallel?
Batteries last longer in parallel, because the voltage remains the same, but the amps increase. If you connect two 12v 50ah batteries in parallel, it will still be a 12 volt system, but the amps will double to 100ah, so the batteries will last longer. On the other hand, when batteries are connected in series, voltage is increased while capacity (ah) stays the same.
Can you put Lifepo4 batteries in series?
It depends on the batteries – if you have Ionic batteries, chances are you can (double check though). Many Lifepo4 batteries can’t be hooked up in series, because they’ll get damaged. But most Ionic lithium batteries are capable of series connections. Not all of them are though, so please check your battery’s user manual to make sure.
Is series or parallel more powerful?
A parallel circuit consumes more power. Compared to series (both having the same voltage), parallel causes much more power to be dissipated by each of the resistors.
Which is safer, series or parallel?
Generally speaking, neither is safer than the other. They’re more or less equally safe. Supply voltage is the main thing that matters there.
Do Batteries Last Longer In Series Or Parallel?
Series connections provide a higher voltage which is slightly more efficient. This means that batteries wired in series can last marginally longer than batteries wired in parallel. However, batteries connected in series vs. parallel will provide roughly the same amount of runtime. Let’s take a look at a quick example that explains why this is true.
Two 12-volt batteries with a 100 Ah capacity are powering a 240-watt device. These two batteries wired in series will provide 24 volts and 100 Ah of capacity. The current draw of the device will be ten amps (24 x 10 = 240). The theoretical runtime of the series system is 100 Ah divided by ten amps, which is ten hours.
Conversely, the same two batteries in parallel provide 12-volts and 200 Ah of capacity. The device’s current draw in this setup is 20 amps (12 x 20 = 240). The theoretical runtime of the parallel system is 200 Ah divided by 20 amps, which is also ten hours.
Can you run two batteries in series and it parallel at the same time?
Can You Wire Batteries in Series and Parallel? You cannot wire the same batteries in series and parallel as you would short the system, but you can wire sets of batteries in series and parallel to create a larger battery bank at a higher voltage.
Is it OK to charge 2 batteries in parallel?
Connecting in parallel stacks up the amp hours of each battery, allowing for a longer use. This type of set-up is for systems that use a lower voltage, but are used for longer periods of time.